Difference between revisions of "ACC"
From Deliberative Democracy Institiute Wiki
(→rostral ACC) |
(→dorsal ACC) |
||
| (41 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | The '''anterior cingulate cortex''' (ACC) is the frontal part of the [[cingulate cortex]], that resembles a "collar" form around the [[corpus callosum]], the fibrous bundle that relays neural signals between the right and left [[cerebral hemisphere]]s of the brain. It consists of Brodmann areas 24, 32 and 33. It appears to play a role in a wide variety of [[Autonomic nervous system|autonomic]] functions, such as regulating blood pressure and heart rate, as well as rational cognitive functions, such as reward anticipation, [[Decision Making|decision making]], empathy<ref>http://ccare.stanford.edu/node/89</ref> and emotion.<ref>Decety, J., & Jackson, P.L. (2004). The functional architecture of human empathy. Behavioral and Cognitive Neuroscience Reviews, 3, 71-100.</ref><ref>Jackson P.L., Brunet E., Meltzoff A.N., Decety J., 2006 Empathy examined through the neural mechanisms involved in imagining how I feel versus how you feel pain: An event-related fMRI study, ''Neuropsychologia'', 44, pp. 752–61</ref> | + | The '''anterior cingulate cortex''' (ACC) is the frontal part of the [[cingulate cortex]], that resembles a "collar" form around the [[corpus callosum]], the fibrous bundle that relays neural signals between the right and left [[cerebral hemisphere]]s of the brain. It consists of Brodmann areas 24, 32 and 33. It appears to play a role in a wide variety of [[Autonomic nervous system|autonomic]] functions, such as regulating blood pressure and heart rate, as well as rational cognitive functions, such as [[rewards|reward]] anticipation, [[Decision Making|decision making]], empathy<ref>http://ccare.stanford.edu/node/89</ref> and emotion.<ref>Decety, J., & Jackson, P.L. (2004). The functional architecture of human empathy. Behavioral and Cognitive Neuroscience Reviews, 3, 71-100.</ref><ref>Jackson P.L., Brunet E., Meltzoff A.N., Decety J., 2006 Empathy examined through the neural mechanisms involved in imagining how I feel versus how you feel pain: An event-related fMRI study, ''Neuropsychologia'', 44, pp. 752–61</ref>. ACC gyrus is involved in learning social values<ref>Rushworth M, Behrens T, Rudebeck P, Walton M. Contrasting roles for cingulate and orbitofrontal cortex in decisions and social behavior. Trends In Cognitive Sciences. 2007;11: 168– 176.</ref>. ACC is also necessary for an appraisal of the energetic cost versus benefits of actions, and a preference to expend effort to achieve a goal. |
| − | In decision making it is thought to detect conflicts between two deductions<ref>[http://www.nature.com/neuro/journal/v10/n10/abs/nn1979.html Neurocognitive correlates of liberalism and conservatism, 2007, Amodio et al. Nature neuroscience] ([http://www.talyaron.com/wiki/index.php?title=Neurocognitive_correlates_of_liberalism_and_conservatism_2007 Summery in Hebrew])</ref><ref>[http://cercor.oxfordjournals.org/content/18/4/796.full Jin Fan, Patrick R. Hof, Kevin G. Guise, John A. Fossella and Michael I. Posner, The Functional Integration of the Anterior Cingulate Cortex during Conflict Processing, Cerebral Cortex, Volume 18 Issue 4, p. 796-805.]</ref> and [[value evaluation in the brain|evaluating]] the [[rewards]] of actions<ref>[http://www.nature.com/neuro/journal/v9/n7/abs/nn1724.html Kennerley et al., Optimal decision making and the anterior cingulate cortex, Nature Neuroscience 9, 940 - 947 (2006)] </ref>. On the integration of these finding please read this [http://www.lamsade.dauphine.fr/~mousseau/pmwiki-2.1.5/uploads/Bibliographie/13.pdf article]. | + | ACC sulcus may be required for learning of [[action]] [[value|values]]<ref>Kennerley SW, Walton ME, Behrens TEJ, Buckley MJ, Rushworth MFS. Optimal decision-making and the anterior cingulate cortex. Nature Neuroscience. 2006;9: 940– 947.</ref>. Similar regions in ACC have also been shown to encode decision uncertainty<ref>Behrens TE, Woolrich MW, Walton ME, Rushworth MF. Learning the value of information in an uncertain world. Nature Neuroscience. 2007;10: 1214–1221.</ref> |
| + | |||
| + | In decision making it is thought to detect conflicts between two deductions<ref>[http://scholar.google.co.il/scholar_url?url=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.nature.com%2Fnature%2Fjournal%2Fv402%2Fn6758%2Ffull%2F402179a0.html&hl=iw&sa=T&oi=gga&ct=gga&cd=1&ei=VFe2VPCmI_Ga0gHkjIGADg&scisig=AAGBfm08okmBFaRTDegwLnaTdSLpsdJcNw&nossl=1&ws=1366x657 Botvinick, M., Nystrom, L. E., Fissell, K., Carter, C. S., & Cohen, J. D. (1999). Conflict monitoring versus selection-for-action in anterior cingulate cortex. Nature, 402(6758), 179–181.]</ref><ref>[http://www.nature.com/neuro/journal/v10/n10/abs/nn1979.html Neurocognitive correlates of liberalism and conservatism, 2007, Amodio et al. Nature neuroscience] ([http://www.talyaron.com/wiki/index.php?title=Neurocognitive_correlates_of_liberalism_and_conservatism_2007 Summery in Hebrew])</ref><ref>[http://cercor.oxfordjournals.org/content/18/4/796.full Jin Fan, Patrick R. Hof, Kevin G. Guise, John A. Fossella and Michael I. Posner, The Functional Integration of the Anterior Cingulate Cortex during Conflict Processing, Cerebral Cortex, Volume 18 Issue 4, p. 796-805.]</ref> and [[value evaluation in the brain|evaluating]] the [[rewards]] of actions<ref>[http://www.nature.com/neuro/journal/v9/n7/abs/nn1724.html Kennerley et al., Optimal decision making and the anterior cingulate cortex, Nature Neuroscience 9, 940 - 947 (2006)] </ref>. On the integration of these finding please read this [http://www.lamsade.dauphine.fr/~mousseau/pmwiki-2.1.5/uploads/Bibliographie/13.pdf article].D1 ([[dopamine]] 1) receptor blockade in ACC reduces preference for expending effort for rats<ref>Schweimer J, Hauber W. Dopamine D1 receptors in the anterior cingulate cortex regulate effort-based decision-making. Learning & Memory. 2006;13: 777–782</ref>. | ||
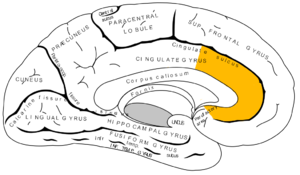
[[File:Gray727 anterior cingulate cortex.png|thumb|alt=Medial surface of left cerebral hemisphere, with anterior cingulate highlighted.|Medial surface of left cerebral hemisphere, with anterior cingulate highlighted.]] | [[File:Gray727 anterior cingulate cortex.png|thumb|alt=Medial surface of left cerebral hemisphere, with anterior cingulate highlighted.|Medial surface of left cerebral hemisphere, with anterior cingulate highlighted.]] | ||
| − | In order to resolve an emotional conflict the rostal[[ACC]] inhibits the amygdala (or [[FFFF]] mechanism)<ref>[http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.126.1555&rep=rep1&type=pdf Amit Etkin, Tobias Egner, Daniel M. Peraza, Eric R. Kandel and Joy Hirsch, Resolving Emotional Conflict: A Role for the Rostral Anterior Cingulate Cortex in Modulating Activity in the Amygdala, Neuron 51, 1–12, September 7, 2006]</ref>. This is strengthing by the findings that in panic disorder, the volume of the the ACC is reduced, <ref>[https://www.slicer.org/slicerWeb/images/2/2c/Asami-PsychiatryClinNeurosci2008.pdf Takeshi et al., Anterior cingulate cortex volume reduction in patients with panic disorder, Psychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences 2008; 62: 322–330]</ref> . When the ACC (ACcd) has deficient in activation, there seem to be more impolsivity in ADHD compered to control group<ref>[http://faculty-web.at.northwestern.edu/speech/booth/james/neuropsychology/AttentionArticles/BushFrazier.1999.pdf low ACcd activity and ADHD impulsivity, 1999]</ref>. When anticipating pain, women domnstrate more activation of the ACC<ref>[http://ukpmc.ac.uk/abstract/MED/16012355/reload=0;jsessionid=fBlS5IiTyyjXq46t6m68.12 Gender difrences in ACC before pain, 2005]</ref>. | + | In order to resolve an emotional conflict the rostal[[ACC]] inhibits the [[amygdala]] (or [[FFFF]] mechanism)<ref>[http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.126.1555&rep=rep1&type=pdf Amit Etkin, Tobias Egner, Daniel M. Peraza, Eric R. Kandel and Joy Hirsch, Resolving Emotional Conflict: A Role for the Rostral Anterior Cingulate Cortex in Modulating Activity in the Amygdala, Neuron 51, 1–12, September 7, 2006]</ref>. This is strengthing by the findings that in panic disorder, the volume of the the ACC is reduced, <ref>[https://www.slicer.org/slicerWeb/images/2/2c/Asami-PsychiatryClinNeurosci2008.pdf Takeshi et al., Anterior cingulate cortex volume reduction in patients with panic disorder, Psychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences 2008; 62: 322–330]</ref> . When the ACC (ACcd) has deficient in activation, there seem to be more impolsivity in ADHD compered to control group<ref>[http://faculty-web.at.northwestern.edu/speech/booth/james/neuropsychology/AttentionArticles/BushFrazier.1999.pdf low ACcd activity and ADHD impulsivity, 1999]</ref>. When anticipating pain, women domnstrate more activation of the ACC<ref>[http://ukpmc.ac.uk/abstract/MED/16012355/reload=0;jsessionid=fBlS5IiTyyjXq46t6m68.12 Gender difrences in ACC before pain, 2005]</ref>. |
| + | |||
| + | It seems that [[LC-NE system|LC-NE]] relese [[Norepinephrine]] to [[ACC]], which then elvate wakeness. The [[ACC]] send signals to the [[LC-NE system|LC]], to maintain wakeness while new stimules are precived<ref>Heinrich S. Gompf, Christine Mathai, Patrick M. Fuller, David A. Wood, Nigel P. Pedersen, Clifford B. Saper, and Jun Lu (2010) Locus Ceruleus and Anterior Cingulate Cortex Sustain Wakefulness in a Novel Environment, The Journal of Neuroscience, 27 October 2010, 30(43): 14543-14551</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | There is a link between ACC activation and [[Larning and pupil size|pupil size]]<ref>[http://hub.hku.hk/handle/10722/179511 Critchley, HD, Tang, J, Glaser, D, Butterworth, B, Dolan, RJ (2005) Anterior cingulate activity during error and autonomic response]</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | reduction in right ACC volume correlates to aggression and defiance<ref>[http://psycnet.apa.org/journals/bne/122/3/677/ Right anterior cingulate: A neuroanatomical correlate of aggression and defiance in boys.]</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==dorsal ACC== | ||
| + | [[dACC]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Hypotheses about its function include guiding reward-based decision making<ref>illiams, Z. M., Bush, G., Rauch, S. L., Cosgrove, G. R. & Eskandar, E. N. Human anterior cingulate neurons and the integration of monetary reward with motor responses. Nature Neurosci.7, 1370–1375 (2004).</ref>, monitoring for conflict between competing responses<ref>otvinick, M., Nystrom, L. E., Fissell, K., Carter, C. S. & Cohen, J. D. Conflict monitoring versus selection-for-action in anterior cingulate cortex. Nature 402, 179–181 (1999)</ref> and predicting task difficulty<ref>rown, J. W. & Braver, T. S. Learned predictions of error likelihood in the anterior cingulate cortex. Science 307, | ||
| + | 1118–1121 (2005)</ref>. Precise mechanisms of dACC function remain unknown. It was found that dACC is involved in adapting behaviour.<ref>[http://ziv.mgh.harvard.edu/pdf/nature11239.pdf Sheth, Sameer A., Matthew K. Mian, Shaun R. Patel, Wael F. Asaad, Ziv M. Williams, Darin D. Dougherty, George Bush, and Emad N. Eskandar. "Human dorsal anterior cingulate cortex neurons mediate ongoing behavioural adaptation." Nature (2012).]</ref>, and help focus attention on the desired option, when conflict arise<ref>[http://cercor.oxfordjournals.org/content/15/2/229.full.pdf+html Weissman, D. H., Gopalakrishnan, A., Hazlett, C. J., & Woldorff, M. G. (2005). Dorsal anterior cingulate cortex resolves conflict from distracting stimuli by boosting attention toward relevant events. Cerebral Cortex, 15(2), 229–237.]</ref>. | ||
| + | |||
| − | + | It is thought that the dorsal ACC is primarly involved in cognitive processing<ref>Bush G, Luu P & Posner MI, Cognotve and emotional influances in the anterior cingulate cotrex, Trends. Cogn. Sci. 4, 215-222 (2000)</ref>. It is part of the learning mechanism, that learn the positive and negative outcomes of actions in neutral tasks<ref>Botvinick M; Nystrom LE; Fissell K; Carter CS; Cohen JD: Conflict monitoring versus selection-for-action in anterior cingulate cortex. Nature 1999; 402:179—181</ref><ref>Kerns JG; Cohen JD; MacDonald AW 3rd; Cho RY; Stenger VA; Carter CS: Anterior cingulate conflict monitoring and adjustments in control. Science 2004; 303:1023—1026</ref><ref>Carter CS; Macdonald AM; Botvinick M; Ross LL; Stenger VA; Noll D; Cohen JD: Parsing executive processes: strategic vs evaluative functions of the anterior cingulate cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2000; 97:1944—1948</ref><ref>Egner T; Hirsch J: The neural correlates and functional integration of cognitive control in a Stroop task. Neuroimage 2005; 24:539—547</ref> and with correlation with rostral ACC, it is involved in emotional learning. It is also a reward mechanism, that gives "globals enrgizing factor", to actions that in the past seems to be rewarding<ref>Struss DT et al.,2005, Multiple frontal systems controlling response speed, ''Neuropshichologia'', 43: 396-417</ref>. Rats with lisions in the ACC, prefer less effortful mission with less reward, to tasks with more effortful with more reward<ref>Walton ME at al, 2003, Fanctional specilization within medial frontal cortex of the antirior cingulate for evaluating effort-related decisions, ''J Neurosci'', 23: 6475-6479</ref>.The ACC motivation mechanism is dependent on dopamin<ref>Assadi SM, Yucel M & Pantelis C, 2009, Dopamin Modulates neural netowrks involved in effort-based decision making, ''Neurosci Biobehav'', 33: 383-393</ref><ref>Alexander MP, 2001, Chronic akinetic mutism after mesanphilic-diancphelick infraction: remediated with dopaminergic medications, ''Neurohabil Nural Repai'', 15:151-156</ref>. | |
| − | It is thought that the dorsal ACC is primarly involved in cognitive processing<ref>Bush G, Luu P & Posner MI, Cognotve and emotional influances in the anterior cingulate cotrex, Trends. Cogn. Sci. 4, 215-222 (2000)</ref>. It is part of the learning mechanism, that learn the positive and negative outcomes of actions. It is also a reward mechanism, that gives "globals enrgizing factor", to actions that in the past seems to be rewarding<ref>Struss DT et al.,2005, Multiple frontal systems controlling response speed, ''Neuropshichologia'', 43: 396-417</ref>. Rats with lisions in the ACC, prefer less effortful mission with less reward, to tasks with more effortful with more reward<ref>Walton ME at al, 2003, Fanctional specilization within medial frontal cortex of the antirior cingulate for evaluating effort-related decisions, ''J Neurosci'', 23: 6475-6479</ref>.The ACC motivation mechanism is dependent on dopamin<ref>Assadi SM, Yucel M & Pantelis C, 2009, Dopamin Modulates neural netowrks involved in effort-based decision making, ''Neurosci Biobehav'', 33: 383-393</ref><ref>Alexander MP, 2001, Chronic akinetic mutism after mesanphilic-diancphelick infraction: remediated with dopaminergic medications, ''Neurohabil Nural Repai'', 15:151-156</ref> | ||
| − | [[A Role for the Human Dorsal Anterior Cingulate Cortex in Fear Expression, 2007]] - dACC has a major role in fear expression. When electrode stimulus was introduced to the dACC during head operations, patients reported high level of anxiety, where as when the regions was removed, anxiety symptoms were reduced<ref>Meyer G, McElhaney M, Martin W, McGraw CP (1973): Stereotactic cin- gulotomy with results of acute stimulation and serial psychological testing, In: Laitinen LV, Livingston KE, editors. Surgical Approaches in Psychiatry. Lancaster, United Kingdom: MTP, Baltimore, 39 –58.</ref> | + | Hypothesis: The Meutation in Dopamin receptor D2 may lower the amount of dopamin recived by the ACC, thus it may be the cause that make people with Atention Deficit Disorder ([[ADD]]), have lack of motivation to engage in effortful actions and decision making. |
| + | |||
| + | [[A Role for the Human Dorsal Anterior Cingulate Cortex in Fear Expression, 2007]] - dACC has a major role in [[fear]] expression. When electrode stimulus was introduced to the dACC during head operations, patients reported high level of anxiety, where as when the regions was removed, anxiety symptoms were reduced<ref>Meyer G, McElhaney M, Martin W, McGraw CP (1973): Stereotactic cin- gulotomy with results of acute stimulation and serial psychological testing, In: Laitinen LV, Livingston KE, editors. Surgical Approaches in Psychiatry. Lancaster, United Kingdom: MTP, Baltimore, 39 –58.</ref>. See also the page on [[fear]]. | ||
[[Dorsal ACC decision making system]] | [[Dorsal ACC decision making system]] | ||
| − | + | ==rostral ACC== | |
| − | It is thought that rostral ACC id involved in emotional processing<ref>Bush G, Luu P & Posner MI, Cognotve and emotional influances in the anterior cingulate cotrex, Trends. Cogn. Sci. 4, 215-222 (2000)</ref>. Sadness enhances the experience of pain via neural [[ACC|activation in the anterior cingulate cortex]] and amygdala<ref>[ http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1053811909012658Atsou et al., Sadness enhances the experience of pain via neural activation in the anteriorcingulatecortex and amygdala: An fMRI study, 2009]</ref>.The Rostral Anterior Cingulate Cortex Modulates the Efficiency of Amygdala-Dependent Fear Learning<ref>[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2880388/ Bissieree et al., The Rostral Anterior Cingulate Cortex Modulates the Efficiency of Amygdala-Dependent Fear Learning, 2008]</ref>. | + | [[rACC]] |
| + | |||
| + | Also called ventral ACC | ||
| + | |||
| + | It is thought that rostral ACC id involved in emotional processing<ref>Bush G, Luu P & Posner MI, Cognotve and emotional influances in the anterior cingulate cotrex, Trends. Cogn. Sci. 4, 215-222 (2000)</ref>. Sadness enhances the experience of pain via neural [[ACC|activation in the anterior cingulate cortex]] and [[amygdala]]<ref>[ http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1053811909012658Atsou et al., Sadness enhances the experience of pain via neural activation in the anteriorcingulatecortex and amygdala: An fMRI study, 2009]</ref>.The Rostral Anterior Cingulate Cortex Modulates the Efficiency of Amygdala-Dependent Fear Learning<ref>[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2880388/ Bissieree et al., The Rostral Anterior Cingulate Cortex Modulates the Efficiency of Amygdala-Dependent Fear Learning, 2008]</ref>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | It seems that rostral ACC is in the side of the critique<ref>Etkin et al., Emotional processing in anterior cingulate and medial prefrontal cortex, 2011</ref> and have negative feedback on selection of actions. it is highly active in depression<ref>Wagner G, Sinsel E, Sobanski T, et al. Cortical inefficiency in patients with unipolar depression: an event-related FMRI study with the Stroop task. ''Biol Psychiatry'' 2006;59:958-65.</ref>. rACC is correlated with error detection<ref>[http://www.pnas.org/content/102/43/15700.full Polli et al, Rostral and dorsal anterior cingulate cortex make dissociable contributions during antisaccade error commission]</ref><ref>[http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/1469-8986.3720216/abstract Kiehl et al, Error processing and the rostral anterior cingulate: An event-related fMRI study, 2000]</ref>. It is used in emotional conflicts<ref>[http://www.cell.com/neuron/abstract/S0896-6273(06)00626-X Etkin A et al.,Resolving Emotional Conflict: A Role for the Rostral Anterior Cingulate Cortex in Modulating Activity in the Amygdala, Neuron, Volume 51, Issue 6, 871-882, 21 September 2006]</ref> but not with neutral conflicts<ref>[http://www.researchgate.net/publication/227853968_Impaired_Conflict_Adaptation_in_an_Emotional_Task_Context_following_Rostral_Anterior_Cingulate_Cortex_Lesions_in_Humans/file/79e414fe432dd9ea2d.pdf Martin E. Maier, Impaired Conflict Adaptation in an Emotional Task Context following Rostral Anterior Cingulate Cortex Lesions in Humans, 2012]</ref><ref>Egner T; Etkin A; Gale S; Hirsch J: Dissociable neural systems resolve conflict from emotional versus nonemotional distracters. Cereb Cortex 2008; 18:1475—1484</ref><ref>Etkin A; Egner T; Peraza DM; Kandel ER; Hirsch J: Resolving emotional conflict: a role for the rostral anterior cingulate cortex in modulating activity in the amygdala. Neuron 2006; 51:871—882</ref>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | rACC is negatively correlated with [[amygdala]] activity in conflict resolution tasks. it is suggested that the rACC down-regulate the amygdala<ref>[http://www.cell.com/neuron/retrieve/pii/S089662730600626X Etkin, A et al. Resolving Emotional Conflict: A Role for the Rostral Anterior Cingulate Cortex in Modulating Activity in the Amygdala, 2006]</ref>. (And may reduce [[anger]] or [[anxiety]]?) | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Liberals and ACC== | ||
| + | [[Conservatives and Liberals|Liberals]] have higher [[ACC]] gray volume<ref>Kanai R, Feilden T, Firth C, Rees G (2011) Political orientations are correlated with brain structure in young adults. Curr Biol 21: 677–680.</ref>. ACC is connected to conflict resultion (rACC to social conflict and dACC to non-social conflict). Reward valence modulates conflict-driven attentional adaptation in the ACC<ref>[http://bernhard-hommel.eu/Van%20Steenbergen%20et%20al.%20(2012).%20Reward%20valence%20modulates%20conflict-driven%20attentional%20adaptation.pdf van Steenbergen, Guido P.H. Band and Bernhard Hommel, Reward valence modulates conflict-driven attentional adaptation: Electrophysiological evidence, 2012]</ref>. ACC appear to encode negatively-valenced components, such as cost or effort<ref>Walton ME, Bannerman DM, Alterescu K, Rushworth MFS. Functional specialization within medial frontal cortex of the anterior cingulate for evaluating effort-related decisions. Journal of Neuroscience. 2003;23: 6475– 6490.</ref>. Greater liberalism was associated with stronger conflict-related [[ACC|anterior cingulate activity]], suggesting greater neurocognitive sensitivity to cues for altering a habitual response pattern, while conservatives have larger volume of right amygdala<ref>[http://www.psych.nyu.edu/amodiolab/Publications_files/Amodio_etal_2007_NatureNeuro.pdf Amodio, D. M., Jost, J. T., Master, S. L., & Yee, C. M. (2007). Neurocognitive correlates of liberalism and conservatism. Nature neuroscience, 10(10), 1246-1247.]</ref><ref>Kanai, R., Feilden, T., Firth, C., & Rees, G. (2011). Political orientations are correlated with brain structure in young adults. Current Biology : CB, 21(8), 677–80. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2011.03.017</ref> As well as more avodience of doing, due to the highten percived costs that the higher volume of the ACC can cause<ref>Suggestion: Tal Yaron, 29/6/2014</ref>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The ACC is important for responce time, therefore it was suggested that the ACC is related to "global energizing factor"<ref>Stuss, Donald T., Michael P. Alexander, Tim Shallice, Terence W. Picton, Malcolm A. Binns, Ronald Macdonald, Agnes Borowiec, and Douglas I. Katz. "Multiple frontal systems controlling response speed." Neuropsychologia 43, no. 3 (2005): 396-417.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ACC is [http://www.scientificamerican.com/article.cfm?id=how-many-friends-can-your-brain-handle enlarged in people with large social networks]. | ||
| − | + | ==Aggresivnce and ACC== | |
| + | Childrens with [[aggression|aggressive]] problems (disruptive behavior disorders) show reduced activity in the ACC<ref>[http://www.international-coaching.org/files/pagini/acc_avb.pdf Gavita, O. A., Capris, D., Bolno, J., & David, D. (2012). Anterior cingulate cortex findings in child disruptive behavior disorders.: A meta-analysis. Aggression and Violent Behavior, 17(6), 507–513.]</ref>. | ||
==Further readings== | ==Further readings== | ||
| Line 25: | Line 57: | ||
* [http://www.princeton.edu/~matthewb/Publications/BotvinickCohenCarter2004.pdf A Research on ACC and conflicit resolution (2004)]. | * [http://www.princeton.edu/~matthewb/Publications/BotvinickCohenCarter2004.pdf A Research on ACC and conflicit resolution (2004)]. | ||
* A paper on [http://brain.oxfordjournals.org/content/125/2/310.full.pdf A paper on ACC and atteintion defliction on pain (2002)]. | * A paper on [http://brain.oxfordjournals.org/content/125/2/310.full.pdf A paper on ACC and atteintion defliction on pain (2002)]. | ||
| + | * An importan article about the social and non-social brain mechanism in autism<ref>[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2993772/ Martino et al., Functional Brain Correlates of Social and Non-Social Processes in Autism Spectrum Disorders: an ALE Meta-Analysis, 2009]</ref>. | ||
==Other close areas== | ==Other close areas== | ||
| Line 34: | Line 67: | ||
[[category: decision making]] | [[category: decision making]] | ||
[[category: Brain regions]] | [[category: Brain regions]] | ||
| + | [[category: brain]] | ||
Latest revision as of 01:31, 15 January 2015
The anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) is the frontal part of the cingulate cortex, that resembles a "collar" form around the corpus callosum, the fibrous bundle that relays neural signals between the right and left cerebral hemispheres of the brain. It consists of Brodmann areas 24, 32 and 33. It appears to play a role in a wide variety of autonomic functions, such as regulating blood pressure and heart rate, as well as rational cognitive functions, such as reward anticipation, decision making, empathy[1] and emotion.[2][3]. ACC gyrus is involved in learning social values[4]. ACC is also necessary for an appraisal of the energetic cost versus benefits of actions, and a preference to expend effort to achieve a goal.
ACC sulcus may be required for learning of action values[5]. Similar regions in ACC have also been shown to encode decision uncertainty[6]
In decision making it is thought to detect conflicts between two deductions[7][8][9] and evaluating the rewards of actions[10]. On the integration of these finding please read this article.D1 (dopamine 1) receptor blockade in ACC reduces preference for expending effort for rats[11].
In order to resolve an emotional conflict the rostalACC inhibits the amygdala (or FFFF mechanism)[12]. This is strengthing by the findings that in panic disorder, the volume of the the ACC is reduced, [13] . When the ACC (ACcd) has deficient in activation, there seem to be more impolsivity in ADHD compered to control group[14]. When anticipating pain, women domnstrate more activation of the ACC[15].
It seems that LC-NE relese Norepinephrine to ACC, which then elvate wakeness. The ACC send signals to the LC, to maintain wakeness while new stimules are precived[16]
There is a link between ACC activation and pupil size[17]
reduction in right ACC volume correlates to aggression and defiance[18]
Contents
dorsal ACC
Hypotheses about its function include guiding reward-based decision making[19], monitoring for conflict between competing responses[20] and predicting task difficulty[21]. Precise mechanisms of dACC function remain unknown. It was found that dACC is involved in adapting behaviour.[22], and help focus attention on the desired option, when conflict arise[23].
It is thought that the dorsal ACC is primarly involved in cognitive processing[24]. It is part of the learning mechanism, that learn the positive and negative outcomes of actions in neutral tasks[25][26][27][28] and with correlation with rostral ACC, it is involved in emotional learning. It is also a reward mechanism, that gives "globals enrgizing factor", to actions that in the past seems to be rewarding[29]. Rats with lisions in the ACC, prefer less effortful mission with less reward, to tasks with more effortful with more reward[30].The ACC motivation mechanism is dependent on dopamin[31][32].
Hypothesis: The Meutation in Dopamin receptor D2 may lower the amount of dopamin recived by the ACC, thus it may be the cause that make people with Atention Deficit Disorder (ADD), have lack of motivation to engage in effortful actions and decision making.
A Role for the Human Dorsal Anterior Cingulate Cortex in Fear Expression, 2007 - dACC has a major role in fear expression. When electrode stimulus was introduced to the dACC during head operations, patients reported high level of anxiety, where as when the regions was removed, anxiety symptoms were reduced[33]. See also the page on fear.
Dorsal ACC decision making system
rostral ACC
Also called ventral ACC
It is thought that rostral ACC id involved in emotional processing[34]. Sadness enhances the experience of pain via neural activation in the anterior cingulate cortex and amygdala[35].The Rostral Anterior Cingulate Cortex Modulates the Efficiency of Amygdala-Dependent Fear Learning[36].
It seems that rostral ACC is in the side of the critique[37] and have negative feedback on selection of actions. it is highly active in depression[38]. rACC is correlated with error detection[39][40]. It is used in emotional conflicts[41] but not with neutral conflicts[42][43][44].
rACC is negatively correlated with amygdala activity in conflict resolution tasks. it is suggested that the rACC down-regulate the amygdala[45]. (And may reduce anger or anxiety?)
Liberals and ACC
Liberals have higher ACC gray volume[46]. ACC is connected to conflict resultion (rACC to social conflict and dACC to non-social conflict). Reward valence modulates conflict-driven attentional adaptation in the ACC[47]. ACC appear to encode negatively-valenced components, such as cost or effort[48]. Greater liberalism was associated with stronger conflict-related anterior cingulate activity, suggesting greater neurocognitive sensitivity to cues for altering a habitual response pattern, while conservatives have larger volume of right amygdala[49][50] As well as more avodience of doing, due to the highten percived costs that the higher volume of the ACC can cause[51].
The ACC is important for responce time, therefore it was suggested that the ACC is related to "global energizing factor"[52]
ACC is enlarged in people with large social networks.
Aggresivnce and ACC
Childrens with aggressive problems (disruptive behavior disorders) show reduced activity in the ACC[53].
Further readings
- An article in a book about theories on the functions of dorsal ACC (2011).
- A Research on ACC and conflicit resolution (2004).
- A paper on A paper on ACC and atteintion defliction on pain (2002).
- An importan article about the social and non-social brain mechanism in autism[54].
Other close areas
- Theory of cognitive dissonance[55]
References
- ↑ http://ccare.stanford.edu/node/89
- ↑ Decety, J., & Jackson, P.L. (2004). The functional architecture of human empathy. Behavioral and Cognitive Neuroscience Reviews, 3, 71-100.
- ↑ Jackson P.L., Brunet E., Meltzoff A.N., Decety J., 2006 Empathy examined through the neural mechanisms involved in imagining how I feel versus how you feel pain: An event-related fMRI study, Neuropsychologia, 44, pp. 752–61
- ↑ Rushworth M, Behrens T, Rudebeck P, Walton M. Contrasting roles for cingulate and orbitofrontal cortex in decisions and social behavior. Trends In Cognitive Sciences. 2007;11: 168– 176.
- ↑ Kennerley SW, Walton ME, Behrens TEJ, Buckley MJ, Rushworth MFS. Optimal decision-making and the anterior cingulate cortex. Nature Neuroscience. 2006;9: 940– 947.
- ↑ Behrens TE, Woolrich MW, Walton ME, Rushworth MF. Learning the value of information in an uncertain world. Nature Neuroscience. 2007;10: 1214–1221.
- ↑ Botvinick, M., Nystrom, L. E., Fissell, K., Carter, C. S., & Cohen, J. D. (1999). Conflict monitoring versus selection-for-action in anterior cingulate cortex. Nature, 402(6758), 179–181.
- ↑ Neurocognitive correlates of liberalism and conservatism, 2007, Amodio et al. Nature neuroscience (Summery in Hebrew)
- ↑ Jin Fan, Patrick R. Hof, Kevin G. Guise, John A. Fossella and Michael I. Posner, The Functional Integration of the Anterior Cingulate Cortex during Conflict Processing, Cerebral Cortex, Volume 18 Issue 4, p. 796-805.
- ↑ Kennerley et al., Optimal decision making and the anterior cingulate cortex, Nature Neuroscience 9, 940 - 947 (2006)
- ↑ Schweimer J, Hauber W. Dopamine D1 receptors in the anterior cingulate cortex regulate effort-based decision-making. Learning & Memory. 2006;13: 777–782
- ↑ Amit Etkin, Tobias Egner, Daniel M. Peraza, Eric R. Kandel and Joy Hirsch, Resolving Emotional Conflict: A Role for the Rostral Anterior Cingulate Cortex in Modulating Activity in the Amygdala, Neuron 51, 1–12, September 7, 2006
- ↑ Takeshi et al., Anterior cingulate cortex volume reduction in patients with panic disorder, Psychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences 2008; 62: 322–330
- ↑ low ACcd activity and ADHD impulsivity, 1999
- ↑ Gender difrences in ACC before pain, 2005
- ↑ Heinrich S. Gompf, Christine Mathai, Patrick M. Fuller, David A. Wood, Nigel P. Pedersen, Clifford B. Saper, and Jun Lu (2010) Locus Ceruleus and Anterior Cingulate Cortex Sustain Wakefulness in a Novel Environment, The Journal of Neuroscience, 27 October 2010, 30(43): 14543-14551
- ↑ Critchley, HD, Tang, J, Glaser, D, Butterworth, B, Dolan, RJ (2005) Anterior cingulate activity during error and autonomic response
- ↑ Right anterior cingulate: A neuroanatomical correlate of aggression and defiance in boys.
- ↑ illiams, Z. M., Bush, G., Rauch, S. L., Cosgrove, G. R. & Eskandar, E. N. Human anterior cingulate neurons and the integration of monetary reward with motor responses. Nature Neurosci.7, 1370–1375 (2004).
- ↑ otvinick, M., Nystrom, L. E., Fissell, K., Carter, C. S. & Cohen, J. D. Conflict monitoring versus selection-for-action in anterior cingulate cortex. Nature 402, 179–181 (1999)
- ↑ rown, J. W. & Braver, T. S. Learned predictions of error likelihood in the anterior cingulate cortex. Science 307, 1118–1121 (2005)
- ↑ Sheth, Sameer A., Matthew K. Mian, Shaun R. Patel, Wael F. Asaad, Ziv M. Williams, Darin D. Dougherty, George Bush, and Emad N. Eskandar. "Human dorsal anterior cingulate cortex neurons mediate ongoing behavioural adaptation." Nature (2012).
- ↑ Weissman, D. H., Gopalakrishnan, A., Hazlett, C. J., & Woldorff, M. G. (2005). Dorsal anterior cingulate cortex resolves conflict from distracting stimuli by boosting attention toward relevant events. Cerebral Cortex, 15(2), 229–237.
- ↑ Bush G, Luu P & Posner MI, Cognotve and emotional influances in the anterior cingulate cotrex, Trends. Cogn. Sci. 4, 215-222 (2000)
- ↑ Botvinick M; Nystrom LE; Fissell K; Carter CS; Cohen JD: Conflict monitoring versus selection-for-action in anterior cingulate cortex. Nature 1999; 402:179—181
- ↑ Kerns JG; Cohen JD; MacDonald AW 3rd; Cho RY; Stenger VA; Carter CS: Anterior cingulate conflict monitoring and adjustments in control. Science 2004; 303:1023—1026
- ↑ Carter CS; Macdonald AM; Botvinick M; Ross LL; Stenger VA; Noll D; Cohen JD: Parsing executive processes: strategic vs evaluative functions of the anterior cingulate cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2000; 97:1944—1948
- ↑ Egner T; Hirsch J: The neural correlates and functional integration of cognitive control in a Stroop task. Neuroimage 2005; 24:539—547
- ↑ Struss DT et al.,2005, Multiple frontal systems controlling response speed, Neuropshichologia, 43: 396-417
- ↑ Walton ME at al, 2003, Fanctional specilization within medial frontal cortex of the antirior cingulate for evaluating effort-related decisions, J Neurosci, 23: 6475-6479
- ↑ Assadi SM, Yucel M & Pantelis C, 2009, Dopamin Modulates neural netowrks involved in effort-based decision making, Neurosci Biobehav, 33: 383-393
- ↑ Alexander MP, 2001, Chronic akinetic mutism after mesanphilic-diancphelick infraction: remediated with dopaminergic medications, Neurohabil Nural Repai, 15:151-156
- ↑ Meyer G, McElhaney M, Martin W, McGraw CP (1973): Stereotactic cin- gulotomy with results of acute stimulation and serial psychological testing, In: Laitinen LV, Livingston KE, editors. Surgical Approaches in Psychiatry. Lancaster, United Kingdom: MTP, Baltimore, 39 –58.
- ↑ Bush G, Luu P & Posner MI, Cognotve and emotional influances in the anterior cingulate cotrex, Trends. Cogn. Sci. 4, 215-222 (2000)
- ↑ [ http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1053811909012658Atsou et al., Sadness enhances the experience of pain via neural activation in the anteriorcingulatecortex and amygdala: An fMRI study, 2009]
- ↑ Bissieree et al., The Rostral Anterior Cingulate Cortex Modulates the Efficiency of Amygdala-Dependent Fear Learning, 2008
- ↑ Etkin et al., Emotional processing in anterior cingulate and medial prefrontal cortex, 2011
- ↑ Wagner G, Sinsel E, Sobanski T, et al. Cortical inefficiency in patients with unipolar depression: an event-related FMRI study with the Stroop task. Biol Psychiatry 2006;59:958-65.
- ↑ Polli et al, Rostral and dorsal anterior cingulate cortex make dissociable contributions during antisaccade error commission
- ↑ Kiehl et al, Error processing and the rostral anterior cingulate: An event-related fMRI study, 2000
- ↑ Etkin A et al.,Resolving Emotional Conflict: A Role for the Rostral Anterior Cingulate Cortex in Modulating Activity in the Amygdala, Neuron, Volume 51, Issue 6, 871-882, 21 September 2006
- ↑ Martin E. Maier, Impaired Conflict Adaptation in an Emotional Task Context following Rostral Anterior Cingulate Cortex Lesions in Humans, 2012
- ↑ Egner T; Etkin A; Gale S; Hirsch J: Dissociable neural systems resolve conflict from emotional versus nonemotional distracters. Cereb Cortex 2008; 18:1475—1484
- ↑ Etkin A; Egner T; Peraza DM; Kandel ER; Hirsch J: Resolving emotional conflict: a role for the rostral anterior cingulate cortex in modulating activity in the amygdala. Neuron 2006; 51:871—882
- ↑ Etkin, A et al. Resolving Emotional Conflict: A Role for the Rostral Anterior Cingulate Cortex in Modulating Activity in the Amygdala, 2006
- ↑ Kanai R, Feilden T, Firth C, Rees G (2011) Political orientations are correlated with brain structure in young adults. Curr Biol 21: 677–680.
- ↑ van Steenbergen, Guido P.H. Band and Bernhard Hommel, Reward valence modulates conflict-driven attentional adaptation: Electrophysiological evidence, 2012
- ↑ Walton ME, Bannerman DM, Alterescu K, Rushworth MFS. Functional specialization within medial frontal cortex of the anterior cingulate for evaluating effort-related decisions. Journal of Neuroscience. 2003;23: 6475– 6490.
- ↑ Amodio, D. M., Jost, J. T., Master, S. L., & Yee, C. M. (2007). Neurocognitive correlates of liberalism and conservatism. Nature neuroscience, 10(10), 1246-1247.
- ↑ Kanai, R., Feilden, T., Firth, C., & Rees, G. (2011). Political orientations are correlated with brain structure in young adults. Current Biology : CB, 21(8), 677–80. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2011.03.017
- ↑ Suggestion: Tal Yaron, 29/6/2014
- ↑ Stuss, Donald T., Michael P. Alexander, Tim Shallice, Terence W. Picton, Malcolm A. Binns, Ronald Macdonald, Agnes Borowiec, and Douglas I. Katz. "Multiple frontal systems controlling response speed." Neuropsychologia 43, no. 3 (2005): 396-417.
- ↑ Gavita, O. A., Capris, D., Bolno, J., & David, D. (2012). Anterior cingulate cortex findings in child disruptive behavior disorders.: A meta-analysis. Aggression and Violent Behavior, 17(6), 507–513.
- ↑ Martino et al., Functional Brain Correlates of Social and Non-Social Processes in Autism Spectrum Disorders: an ALE Meta-Analysis, 2009
- ↑ Festinger, L. (1957). A theory ofcognitive dissonance. Evanston, IL: Row, Peterson