Difference between revisions of "Neuronal decision making model"
From Deliberative Democracy Institiute Wiki
(→Basic Mechanism) |
(→Value) |
||
| (23 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{en|[[User:WinSysop|Tal Yaron]] 14:55, 22 June 2014 (IDT)}} |
==Basic Mechanism== | ==Basic Mechanism== | ||
| − | The personal mechanism of decision making is based on [[evaluative neural network]] ( | + | The personal mechanism of decision making is based on [[ENN|evaluative neural network]] (ENN). ENN has two or more paths for reaching a goal. |
| − | [[File:Neural_network_two_paths.jpg|500px | + | [[File:Neural_network_two_paths.jpg|500px|center]] |
| − | For every [[node]] in a path, there are several [[implications]]. Every implication | + | For every [[node]] in a path, there are several [[implications]]. Every implication is attached at the end of it to a reward in the reward system. |
| − | [[File:Neural network two paths implications.jpg|500px | + | ===Value=== |
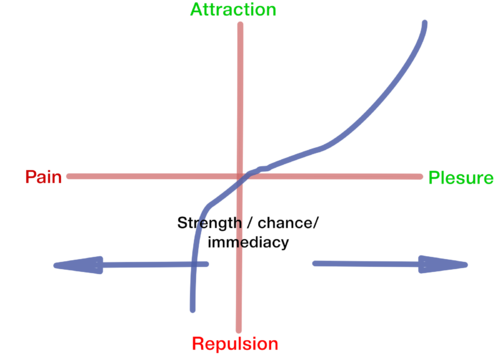
| + | The [[value]] of the reward is signaled by the plesentness or pain of the reward. The magnitude of the reward will be determined by the volume of the of nuronal signaling that is connected to the reward and the intensety of nuronal firing. The amount of siganling, is due to the learning process [[LTP]] and [[STP]]. It will be composed of the chance for the expected results, and the immdiacy. the higher the chances, and the more immidate the results is axpected to be, the stronger the signal will be. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Pain and plesure are not equal. For most of the people, pain will cause more repalsion then plesure will cause attraction. This is due to the hazardous nature of pain. This may be the neuronal mechanism behind [[loss aversion]]. The reward attraction function seems to be the basic mechanisms of the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Prospect_theory prospect theory]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Attraction.png|500px|center|The reward-attraction function model]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Factors Affecting Perception of Value==== | ||
| + | =====Risk of Pain===== | ||
| + | It seems that there are mechanisms that relate to [[FFFF]] mode of thought that will casue people in ''fight'' mode to reduce the expected chances that painful outcomes will result, and also they will feel less pain, therefore they will take more [[risk taking|risks]]. On the other hand, people in the ''flight'' or ''fright'' mode will percieve the likelihood of painful results as much higher and they will feel pain much more, therefore they will avoid risk more then the avarage person. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The amount of exposoure to risks, can also change the percived risk. The media can expose us to danger, to result unjustified fears and risk avodidence. on the other hand, in war time or in highly conservatives coutries, showing the bravery of the hero, without showin the damge it could suffer, will result a tendncy to taking risks. | ||
| + | |||
| + | A need to hury, may also reduce the perceptption of the chances to get injuerd, and also elevate risk taking. | ||
| + | |||
| + | =====Need for Pleasure===== | ||
| + | |||
| + | In satate of addiction, when the the concentration of the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Receptor_%28biochemistry%29 receptors] for pleasure signals is low, people will be more attracted to plesure, and will be ready to take more risks. [[Dopamine]] is a mediator of plesure, and Dopamine agonists are used, thet can cause pathological gambling behavior<ref>Gallagher DA, O’Sullivan SS, Evans AH, Lees AJ, Schrag A. Pathological gambling in Parkinson’s disease: Risk factors and differences from dopamine dysregulation An analysis of published case series. Movement Disorders. 2007;22: 1757– 1763.</ref>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Also, when pain is common and plesure is scarce, people will take more risks, to achieve pleasure. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Choosing Between Options=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Usually people will have in their [[ENN]] one or two roots to achieve a reward. Usually the preferred root will be the one which carry the highest overall values. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Neural network two paths implications.jpg|500px|center]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | For instance, if we want to feel good with ourselves, and we have to decide between eating chocolate cake or tomato, we will usually choose the cake. The reason is that the reward from the cake is much faster and sure, whereas reward from being slim, is distant and very shaky. Also, in the "cake" root, we will have to suffer from feeling of hunger. To overcome this natural decision making root, we may use a strong inhibition of the cake root, or with mental tricks that make us feel more disgust by cakes and more alive with vegetables. | ||
==Elements Influencing ENN== | ==Elements Influencing ENN== | ||
| − | '''[[FFFF]]''' and '''[[exploitation]]''' will heighten the threshold for using paths, therefore only strongest path will be used. If there aren't very strong paths available, no path will be selected, and the decision making system will freeze. | + | ===Raising paths threshold=== |
| + | |||
| + | '''[[FFFF]]''' and '''[[exploitation]]''' will heighten the threshold for using paths, therefore only the strongest path will be used. If there aren't very strong paths available, no path will be selected, and the decision making system will freeze. When a person is in a feeling of threat, it will activate [[FFFF]], that will lower the threshold. Any attack on the [[ego]], can produce feeling of attack. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Lowering paths threshold=== | ||
| + | '''[[PFC]]''' and '''[[exploration]]''' on the other side of the scale will reduce the threshold, and therefore will enable a larger variety of options. The option that will be selected will be the one with the most rewards in non-self-control mode. In self-control mode, greater rewards in the future will be preferred to immediate high rewards. | ||
'''[[RPE]]''' will produce lower the threshold even more, which will result even higher diversity in the paths. | '''[[RPE]]''' will produce lower the threshold even more, which will result even higher diversity in the paths. | ||
| − | == | + | ===Creating Strong Paths=== |
| − | + | The strongest path will be produced by conducting more repetitions in this path relative to other paths, therfore it will be more [[corroborate|corroborated]] | |
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
[[social decision making model]] | [[social decision making model]] | ||
| + | [[nural decision makeing - brain]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==References== | ||
| + | <references/> | ||
[[category: decision making]] | [[category: decision making]] | ||
| + | [[category: decision making model]] | ||
[[category: deliberation]] | [[category: deliberation]] | ||
[[category: theory]] | [[category: theory]] | ||
Latest revision as of 07:06, 9 February 2016
|
This page was writen by a non-English speeking writer. Please help us improve the quality of the paper.Tal Yaron 14:55, 22 June 2014 (IDT) |
Contents
Basic Mechanism
The personal mechanism of decision making is based on evaluative neural network (ENN). ENN has two or more paths for reaching a goal.
For every node in a path, there are several implications. Every implication is attached at the end of it to a reward in the reward system.
Value
The value of the reward is signaled by the plesentness or pain of the reward. The magnitude of the reward will be determined by the volume of the of nuronal signaling that is connected to the reward and the intensety of nuronal firing. The amount of siganling, is due to the learning process LTP and STP. It will be composed of the chance for the expected results, and the immdiacy. the higher the chances, and the more immidate the results is axpected to be, the stronger the signal will be.
Pain and plesure are not equal. For most of the people, pain will cause more repalsion then plesure will cause attraction. This is due to the hazardous nature of pain. This may be the neuronal mechanism behind loss aversion. The reward attraction function seems to be the basic mechanisms of the prospect theory.
Factors Affecting Perception of Value
Risk of Pain
It seems that there are mechanisms that relate to FFFF mode of thought that will casue people in fight mode to reduce the expected chances that painful outcomes will result, and also they will feel less pain, therefore they will take more risks. On the other hand, people in the flight or fright mode will percieve the likelihood of painful results as much higher and they will feel pain much more, therefore they will avoid risk more then the avarage person.
The amount of exposoure to risks, can also change the percived risk. The media can expose us to danger, to result unjustified fears and risk avodidence. on the other hand, in war time or in highly conservatives coutries, showing the bravery of the hero, without showin the damge it could suffer, will result a tendncy to taking risks.
A need to hury, may also reduce the perceptption of the chances to get injuerd, and also elevate risk taking.
Need for Pleasure
In satate of addiction, when the the concentration of the receptors for pleasure signals is low, people will be more attracted to plesure, and will be ready to take more risks. Dopamine is a mediator of plesure, and Dopamine agonists are used, thet can cause pathological gambling behavior[1].
Also, when pain is common and plesure is scarce, people will take more risks, to achieve pleasure.
Choosing Between Options
Usually people will have in their ENN one or two roots to achieve a reward. Usually the preferred root will be the one which carry the highest overall values.
For instance, if we want to feel good with ourselves, and we have to decide between eating chocolate cake or tomato, we will usually choose the cake. The reason is that the reward from the cake is much faster and sure, whereas reward from being slim, is distant and very shaky. Also, in the "cake" root, we will have to suffer from feeling of hunger. To overcome this natural decision making root, we may use a strong inhibition of the cake root, or with mental tricks that make us feel more disgust by cakes and more alive with vegetables.
Elements Influencing ENN
Raising paths threshold
FFFF and exploitation will heighten the threshold for using paths, therefore only the strongest path will be used. If there aren't very strong paths available, no path will be selected, and the decision making system will freeze. When a person is in a feeling of threat, it will activate FFFF, that will lower the threshold. Any attack on the ego, can produce feeling of attack.
Lowering paths threshold
PFC and exploration on the other side of the scale will reduce the threshold, and therefore will enable a larger variety of options. The option that will be selected will be the one with the most rewards in non-self-control mode. In self-control mode, greater rewards in the future will be preferred to immediate high rewards.
RPE will produce lower the threshold even more, which will result even higher diversity in the paths.
Creating Strong Paths
The strongest path will be produced by conducting more repetitions in this path relative to other paths, therfore it will be more corroborated
See Also
nural decision makeing - brain
References
- ↑ Gallagher DA, O’Sullivan SS, Evans AH, Lees AJ, Schrag A. Pathological gambling in Parkinson’s disease: Risk factors and differences from dopamine dysregulation An analysis of published case series. Movement Disorders. 2007;22: 1757– 1763.