Difference between revisions of "VTA"
From Deliberative Democracy Institiute Wiki
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[file:VTA.gif|300px|right]] | [[file:VTA.gif|300px|right]] | ||
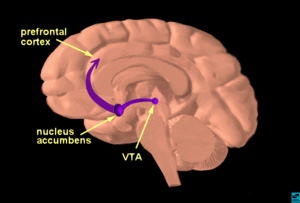
Ventral tegmental area (VTA) is a group of neurons located close to the midline on the floor of the midbrain (mesencephalon). The VTA is the origin of the [[dopamine|dopaminergic]] cell bodies of the mesocorticolimbic dopamine system and is widely implicated in the drug and natural reward circuitry of the brain. It is important in cognition, motivation, orgasm, drug addiction, intense emotions relating to love, and several psychiatric disorders. The VTA contains neurons that project to numerous areas of the brain, from the prefrontal cortex ([[PFC]]) to the caudal brainstem and several regions in between. | Ventral tegmental area (VTA) is a group of neurons located close to the midline on the floor of the midbrain (mesencephalon). The VTA is the origin of the [[dopamine|dopaminergic]] cell bodies of the mesocorticolimbic dopamine system and is widely implicated in the drug and natural reward circuitry of the brain. It is important in cognition, motivation, orgasm, drug addiction, intense emotions relating to love, and several psychiatric disorders. The VTA contains neurons that project to numerous areas of the brain, from the prefrontal cortex ([[PFC]]) to the caudal brainstem and several regions in between. | ||
| + | |||
| + | VTA/SN could act as a hub to compare predicted action values and obtained outcomes (see also [[RPE]]). | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
[[category: brain]] | [[category: brain]] | ||
Revision as of 00:00, 30 June 2014
Ventral tegmental area (VTA) is a group of neurons located close to the midline on the floor of the midbrain (mesencephalon). The VTA is the origin of the dopaminergic cell bodies of the mesocorticolimbic dopamine system and is widely implicated in the drug and natural reward circuitry of the brain. It is important in cognition, motivation, orgasm, drug addiction, intense emotions relating to love, and several psychiatric disorders. The VTA contains neurons that project to numerous areas of the brain, from the prefrontal cortex (PFC) to the caudal brainstem and several regions in between.
VTA/SN could act as a hub to compare predicted action values and obtained outcomes (see also RPE).