Difference between revisions of "Neuronal decision making model"
From Deliberative Democracy Institiute Wiki
(→Basic Mechanism) |
(→Basic Mechanism) |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
[[File:Neural_network_two_paths.jpg|500px|thumb|center]] | [[File:Neural_network_two_paths.jpg|500px|thumb|center]] | ||
| − | For every [[node]] in a path, there are several [[implications]]. Every implication | + | For every [[node]] in a path, there are several [[implications]]. Every implication is attached at the end of it to a reward in the reward system. |
| + | |||
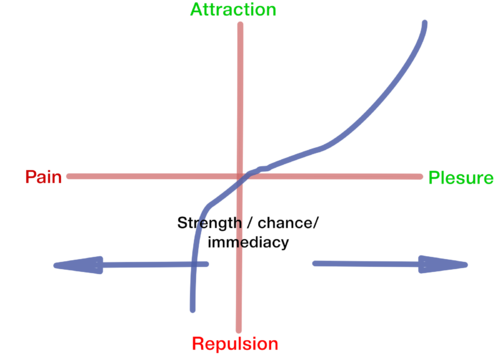
| + | The [[value]] of the reward is signaled by the plesentness or pain of the reward, the magnitude of the reward, the chance of the reward and it's immdiecy. The more pleasent the expectd reward is, the more we will be attracted to it. The more pain we assume the reward will bring, the less we will like to chose this reward. When pain in in stake, we will be rpulsed by it more then an equivelnt amount of plesure.. The stongger the reward will be the more we will be attracted to it, if pleasent, or we will distance ourselves from it. The faster we will think we will get the reward, the more we will be chose to take it's course. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Attraction.png|500px|center|The reward-attraction function model]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | the expected reward, and the faster the | ||
| + | a value which is represented by the [[reward system]]. the value can very from positive to negative. The strength of the reward will be composed by the intensity of the reward that the reward system cell produce, and the closeness of the reward to the action, where immediate reward will increase the strength of the reward to the implication, while delayed reward will result reduced connection between implication and reward. The strength will be produced according to the learning rules of [[LTP]] and [[STP]]. | ||
[[File:Neural network two paths implications.jpg|500px|thumb|center]] | [[File:Neural network two paths implications.jpg|500px|thumb|center]] | ||
Revision as of 09:18, 20 June 2014
|
This page is a stub. It is not ready for publication and is used to aggregate information about a subject. You can add further reading and add information to the page. If you want to prepare this page for publication please consults with the creator of this page. |
Contents
Basic Mechanism
The personal mechanism of decision making is based on evaluative neural network (ENN). ENN has two or more paths for reaching a goal.
For every node in a path, there are several implications. Every implication is attached at the end of it to a reward in the reward system.
The value of the reward is signaled by the plesentness or pain of the reward, the magnitude of the reward, the chance of the reward and it's immdiecy. The more pleasent the expectd reward is, the more we will be attracted to it. The more pain we assume the reward will bring, the less we will like to chose this reward. When pain in in stake, we will be rpulsed by it more then an equivelnt amount of plesure.. The stongger the reward will be the more we will be attracted to it, if pleasent, or we will distance ourselves from it. The faster we will think we will get the reward, the more we will be chose to take it's course.
the expected reward, and the faster the a value which is represented by the reward system. the value can very from positive to negative. The strength of the reward will be composed by the intensity of the reward that the reward system cell produce, and the closeness of the reward to the action, where immediate reward will increase the strength of the reward to the implication, while delayed reward will result reduced connection between implication and reward. The strength will be produced according to the learning rules of LTP and STP.
Elements Influencing ENN
FFFF and exploitation will heighten the threshold for using paths, therefore only strongest path will be used. If there aren't very strong paths available, no path will be selected, and the decision making system will freeze. The strongest path will be produced by conducting more repetitions in this path relative to other paths. PFC and exploration on the other side of the scale will reduce the threshold, and therefore will enable a larger variety of options. the option that will be selected will be the one with the most rewards in non-self control mode. In self-control mode, a grater rewards in the future will be preferred to immediate high rewards.
RPE will produce lower the threshold even more, which will result even higher diversity in the paths.
Inducing changes in the Threshold of the Paths
When a person is in a feeling of threat, it will activate FFFF, that will lower the threshold. Any attack on the ego, can produce feeling of attack.