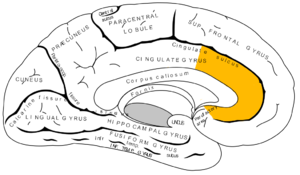
The anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) is the frontal part of the cingulate cortex, that resembles a "collar" form around the corpus callosum, the fibrous bundle that relays neural signals between the right and left cerebral hemispheres of the brain. It consists of Brodmann areas 24, 32 and 33. It appears to play a role in a wide variety of autonomic functions, such as regulating blood pressure and heart rate, as well as rational cognitive functions, such as reward anticipation, decision making, empathy[1] and emotion.[2][3]
In decision making it is thought to detect conflicts between two deductions[4][5] and evaluating the rewards of actions[6]. On the integration of these finding please read this article.
In order to resolve an emotional conflict the rostalACC inhibits the amygdala (or FFFF mechanism)[7]. This is strengthing by the findings that in panic disorder, the volume of the the ACC is reduced, [8] . When the ACC (ACcd) has deficient in activation, there seem to be more impolsivity in ADHD compered to control group[9]. When anticipating pain, women domnstrate more activation of the ACC[10].
An article in a book about theories on the functions of dorsal ACC (2011)
Other close areas
- Theory of cognitive dissonance[11]
References
- ↑ http://ccare.stanford.edu/node/89
- ↑ Decety, J., & Jackson, P.L. (2004). The functional architecture of human empathy. Behavioral and Cognitive Neuroscience Reviews, 3, 71-100.
- ↑ Jackson P.L., Brunet E., Meltzoff A.N., Decety J., 2006 Empathy examined through the neural mechanisms involved in imagining how I feel versus how you feel pain: An event-related fMRI study, Neuropsychologia, 44, pp. 752–61
- ↑ Neurocognitive correlates of liberalism and conservatism, 2007, Amodio et al. Nature neuroscience (Summery in Hebrew)
- ↑ Jin Fan, Patrick R. Hof, Kevin G. Guise, John A. Fossella and Michael I. Posner, The Functional Integration of the Anterior Cingulate Cortex during Conflict Processing, Cerebral Cortex, Volume 18 Issue 4, p. 796-805.
- ↑ Kennerley et al., Optimal decision making and the anterior cingulate cortex, Nature Neuroscience 9, 940 - 947 (2006)
- ↑ Amit Etkin, Tobias Egner, Daniel M. Peraza, Eric R. Kandel and Joy Hirsch, Resolving Emotional Conflict: A Role for the Rostral Anterior Cingulate Cortex in Modulating Activity in the Amygdala, Neuron 51, 1–12, September 7, 2006
- ↑ Takeshi et al., Anterior cingulate cortex volume reduction in patients with panic disorder, Psychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences 2008; 62: 322–330
- ↑ low ACcd activity and ADHD impulsivity, 1999
- ↑ Gender difrences in ACC before pain, 2005
- ↑ Festinger, L. (1957). A theory ofcognitive dissonance. Evanston, IL: Row, Peterson