Difference between revisions of "ACC"
From Deliberative Democracy Institiute Wiki
m |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
The '''anterior cingulate cortex''' (ACC) is the frontal part of the [[cingulate cortex]], that resembles a "collar" form around the [[corpus callosum]], the fibrous bundle that relays neuron|neural signals between the right and left [[cerebral hemisphere]]s of the brain. It consists of Brodmann areas 24, 32 and 33. It appears to play a role in a wide variety of [[Autonomic nervous system|autonomic]] functions, such as regulating blood pressure and heart rate, as well as rational cognitive functions, such as reward anticipation, [[Decision Making|decision making]], empathy<ref>http://ccare.stanford.edu/node/89</ref> and emotion.<ref>Decety, J., & Jackson, P.L. (2004). The functional architecture of human empathy. Behavioral and Cognitive Neuroscience Reviews, 3, 71-100.</ref><ref>Jackson P.L., Brunet E., Meltzoff A.N., Decety J., 2006 Empathy examined through the neural mechanisms involved in imagining how I feel versus how you feel pain: An event-related fMRI study, ''Neuropsychologia'', 44, pp. 752–61</ref> | The '''anterior cingulate cortex''' (ACC) is the frontal part of the [[cingulate cortex]], that resembles a "collar" form around the [[corpus callosum]], the fibrous bundle that relays neuron|neural signals between the right and left [[cerebral hemisphere]]s of the brain. It consists of Brodmann areas 24, 32 and 33. It appears to play a role in a wide variety of [[Autonomic nervous system|autonomic]] functions, such as regulating blood pressure and heart rate, as well as rational cognitive functions, such as reward anticipation, [[Decision Making|decision making]], empathy<ref>http://ccare.stanford.edu/node/89</ref> and emotion.<ref>Decety, J., & Jackson, P.L. (2004). The functional architecture of human empathy. Behavioral and Cognitive Neuroscience Reviews, 3, 71-100.</ref><ref>Jackson P.L., Brunet E., Meltzoff A.N., Decety J., 2006 Empathy examined through the neural mechanisms involved in imagining how I feel versus how you feel pain: An event-related fMRI study, ''Neuropsychologia'', 44, pp. 752–61</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | In decision making it is thought to detect conflicts between two deductions<ref>[http://www.nature.com/neuro/journal/v10/n10/abs/nn1979.html Neurocognitive correlates of liberalism and conservatism, 2007, Amodio et al. Nature neuroscience] ([http://www.talyaron.com/wiki/index.php?title=Neurocognitive_correlates_of_liberalism_and_conservatism_2007 Summery in Hebrew])</ref>. | ||
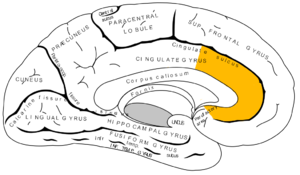
[[File:Gray727 anterior cingulate cortex.png|thumb|alt=Medial surface of left cerebral hemisphere, with anterior cingulate highlighted.|Medial surface of left cerebral hemisphere, with anterior cingulate highlighted.]] | [[File:Gray727 anterior cingulate cortex.png|thumb|alt=Medial surface of left cerebral hemisphere, with anterior cingulate highlighted.|Medial surface of left cerebral hemisphere, with anterior cingulate highlighted.]] | ||
Revision as of 07:27, 10 August 2012
The anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) is the frontal part of the cingulate cortex, that resembles a "collar" form around the corpus callosum, the fibrous bundle that relays neuron|neural signals between the right and left cerebral hemispheres of the brain. It consists of Brodmann areas 24, 32 and 33. It appears to play a role in a wide variety of autonomic functions, such as regulating blood pressure and heart rate, as well as rational cognitive functions, such as reward anticipation, decision making, empathy[1] and emotion.[2][3]
In decision making it is thought to detect conflicts between two deductions[4].
References
- ↑ http://ccare.stanford.edu/node/89
- ↑ Decety, J., & Jackson, P.L. (2004). The functional architecture of human empathy. Behavioral and Cognitive Neuroscience Reviews, 3, 71-100.
- ↑ Jackson P.L., Brunet E., Meltzoff A.N., Decety J., 2006 Empathy examined through the neural mechanisms involved in imagining how I feel versus how you feel pain: An event-related fMRI study, Neuropsychologia, 44, pp. 752–61
- ↑ Neurocognitive correlates of liberalism and conservatism, 2007, Amodio et al. Nature neuroscience (Summery in Hebrew)