Difference between revisions of "ACC"
From Deliberative Democracy Institiute Wiki
(→Other close areas=) |
|||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
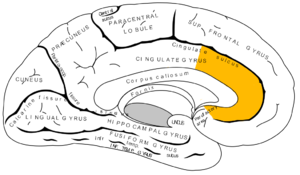
[[File:Gray727 anterior cingulate cortex.png|thumb|alt=Medial surface of left cerebral hemisphere, with anterior cingulate highlighted.|Medial surface of left cerebral hemisphere, with anterior cingulate highlighted.]] | [[File:Gray727 anterior cingulate cortex.png|thumb|alt=Medial surface of left cerebral hemisphere, with anterior cingulate highlighted.|Medial surface of left cerebral hemisphere, with anterior cingulate highlighted.]] | ||
| − | ==Other close areas=== | + | ===Other close areas=== |
| − | * | + | * Theory ofcognitive dissonance<ref>Festinger, L. (1957). A theory ofcognitive dissonance. Evanston, IL: Row, Peterson</ref> |
| − | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Revision as of 01:54, 21 August 2012
The anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) is the frontal part of the cingulate cortex, that resembles a "collar" form around the corpus callosum, the fibrous bundle that relays neural signals between the right and left cerebral hemispheres of the brain. It consists of Brodmann areas 24, 32 and 33. It appears to play a role in a wide variety of autonomic functions, such as regulating blood pressure and heart rate, as well as rational cognitive functions, such as reward anticipation, decision making, empathy[1] and emotion.[2][3]
In decision making it is thought to detect conflicts between two deductions[4] and evaluating the rewards of actions[5]. On the integration of these finding please read this article.
Other close areas
- Theory ofcognitive dissonance[6]
References
- ↑ http://ccare.stanford.edu/node/89
- ↑ Decety, J., & Jackson, P.L. (2004). The functional architecture of human empathy. Behavioral and Cognitive Neuroscience Reviews, 3, 71-100.
- ↑ Jackson P.L., Brunet E., Meltzoff A.N., Decety J., 2006 Empathy examined through the neural mechanisms involved in imagining how I feel versus how you feel pain: An event-related fMRI study, Neuropsychologia, 44, pp. 752–61
- ↑ Neurocognitive correlates of liberalism and conservatism, 2007, Amodio et al. Nature neuroscience (Summery in Hebrew)
- ↑ Kennerley et al., Optimal decision making and the anterior cingulate cortex, Nature Neuroscience 9, 940 - 947 (2006)
- ↑ Festinger, L. (1957). A theory ofcognitive dissonance. Evanston, IL: Row, Peterson